Presentation at the 13th White Rabbit Workshop 2024 at CERN in Geneva, Switzerland, Mar. 21-22, 2024
White Rabbit is a technology that allows to synchronize networked devices or endpoints tens of kilometers apart with a sub-nanosecond accuracy. With minor, but incompatible changes, it is now fully integrated into the IEEE1588-2019 or PTP v2.1 standard as high accuracy (HA) profile.
Each endpoint employs frequency and phase measurement and adjustment techniques using field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) and external voltage-controlled crystal oscillators (VCXOs). This usually requires external circuit boards with specific components not available on commercially off-the-shelf (COTS) development boards.
We implemented White Rabbit nodes on multiple development boards, e.g. AMD ZC706 and ZCU102, only using the FPGA’s resources such as either Mixed-Mode Clock Managers (MMCMs) on the ZC706 or Quad Phase-Locked-Loops (QPLL) on the ZCU102, capable of fully synchronizing with other White Rabbit hardware, such as a Seven Solutions White Rabbit switch (WRS 3/18).
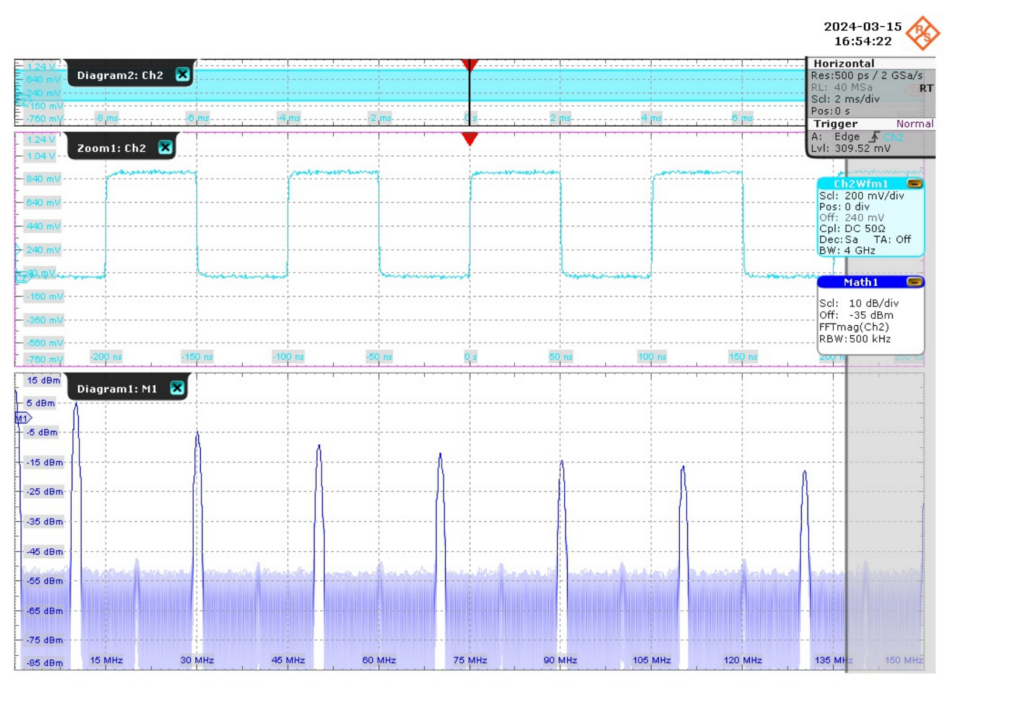
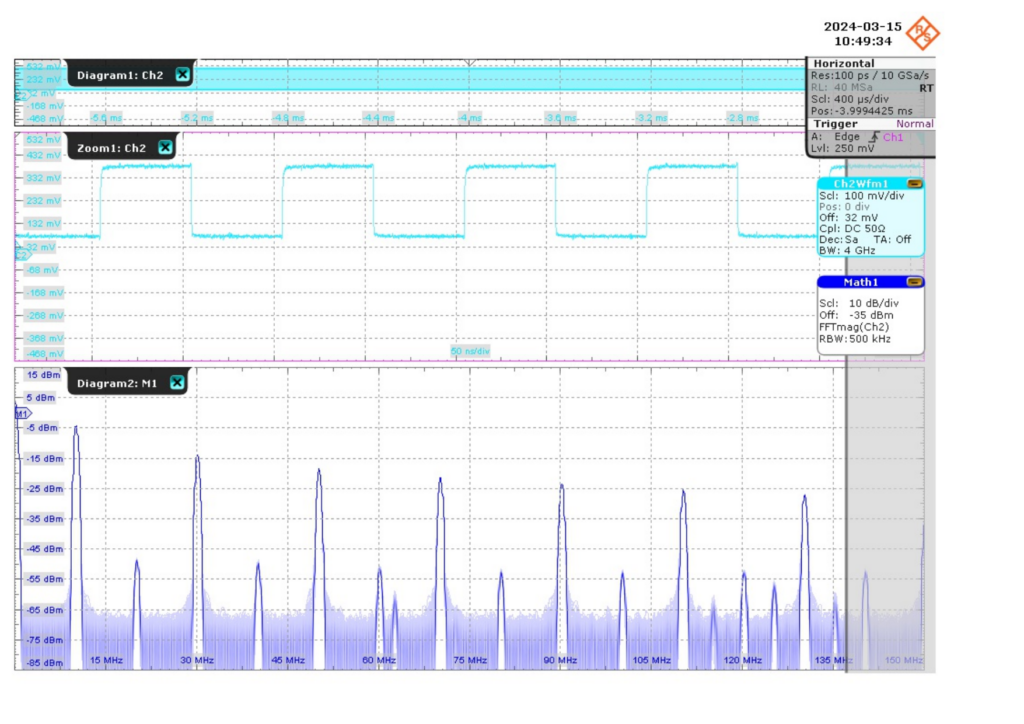
We also compared our synchronized endpoints on the ZCU102 and ZC706 to the timing source of the White Rabbit switch. We obtained initial experimental results of our two VCXO-less White Rabbit implementations using a time interval counter (TIC) for measuring the generated pulse-per-second (PPS) signal and a custom Digital Dual Mixer Time Difference (D-DMTD) circuit for the 10 MHz signal. To validate our measurement approach, we also did a spectrum analysis and a time-interval error analysis of the 10 MHz signals with a professional Rohde&Schwarz RTO1044 oscilloscope.
To learn more about the details, download the slides below or contact us for more informaiton.