FFRAID
100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID

FFRAID: Accelerate FPGA-based NVMe RAID Data Recording and Replay
Some High-Speed Data Acquisition Systems do require storing the data in non-volatile memory. For those cases where the read/write data rate exceeds the capabilities of even the highest performance NVMe SSDs, MLE has developed an NVMe Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID) solution:
Now, you can transfer bulky data from multiple sensors to a RAID of NVMe SSDs at speeds up to 400 Gbps. MLE’s Fast FPGA RAID implements a channel-based architecture, supports data-in-motion pre- and post-processing and is highly scalable with regards to bandwidth and recording capacity. Multiple systems can further be cascaded via high-accuracy IEEE time-synchronization for faster or deeper recording.
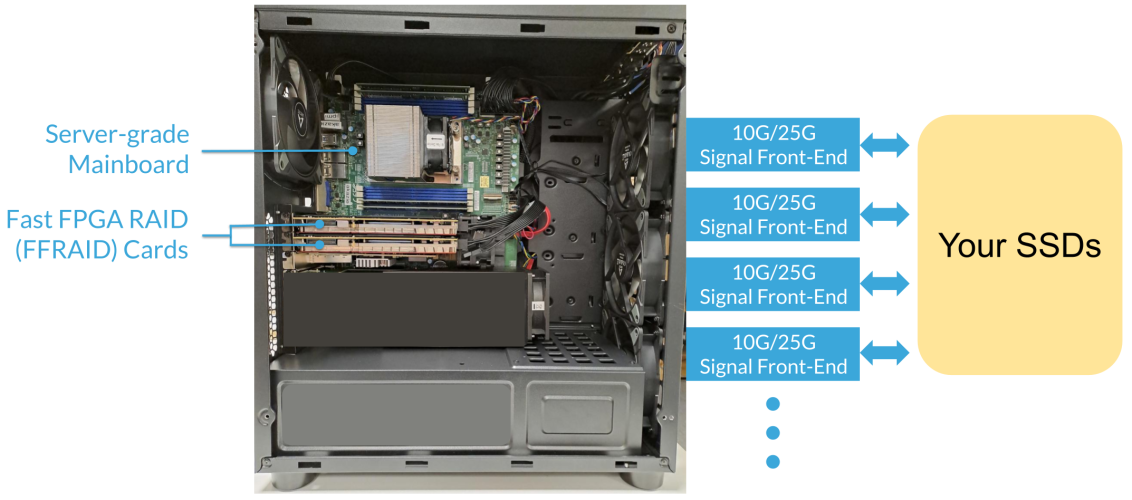
Adaptable signal front-ends support many different I/O standards in a “mix & match” fashion.
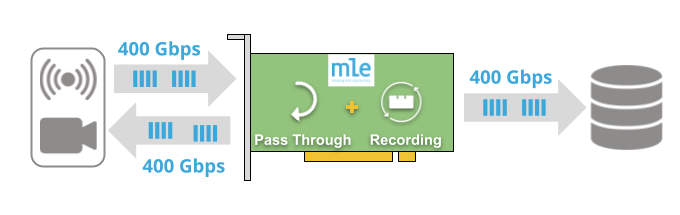
MLE’s Fast FPGA RAID is compatible with Linux Software-RAID (via the Linux MD driver). This allows recording at high data rates and replaying at slower speeds, or vice versa.
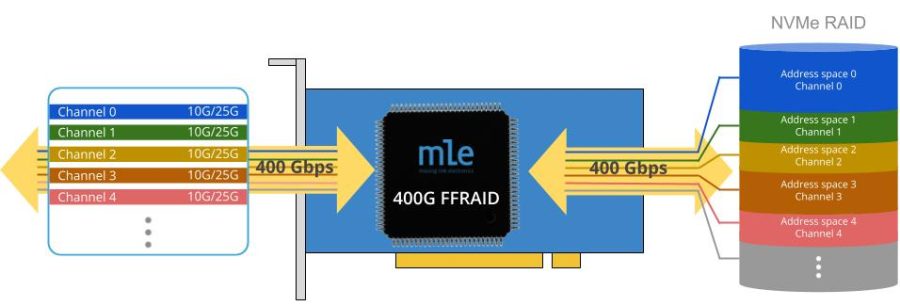
Channel-based Architecture of Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID)
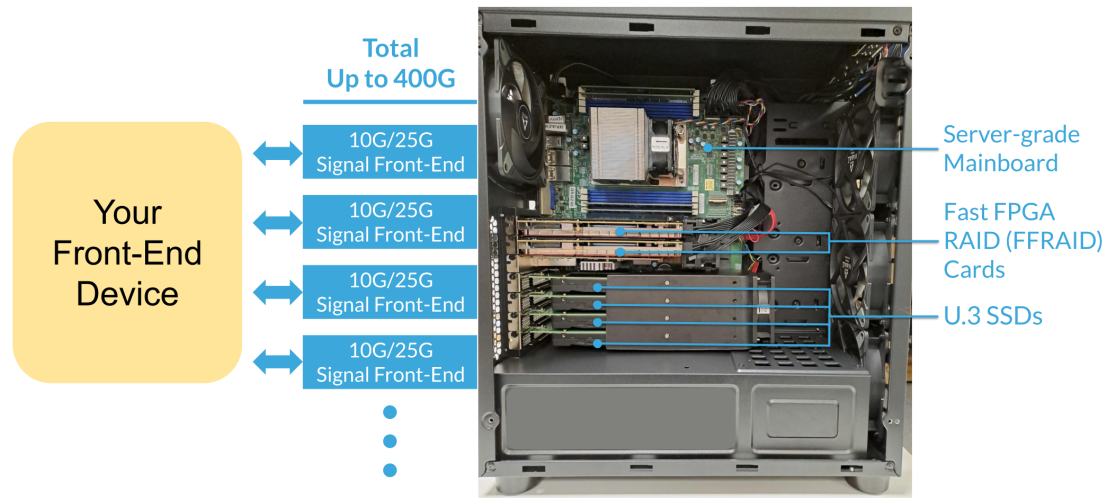
MLE’s Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID) implements a channel-based architecture where each data source/sink can be associated with a dedicated RAID engine and a dedicated storage space. Each channel can have 10/25/50/75/100 Gbps, or combinations thereof.
This channel-based architecture along with the combination of FPGA NVMe Recording Stack plus a well-tuned PCIe setup, delivers a best-in-class price/performance ratio for high-speed data acquisition, recording and replay. MLE’s multi-core NVMe Host Controller Subsystem supports dedicated NVMe queues per SSD in a PCIe Peer-to-Peer communication.
Applications
-
- Autonomous Vehicle Path Record & Replay
- Automotive / Medical / Industrial Test Equipment
- High-speed Radar / Lidar / Camera Data Acquisition & Storage
- Very Deep Network Packet Capture of Ethernet or IPv4 or TCP/UDP Data
Key Features
- Scalable from 100Gbps to 400Gbps
- Cascading of multiple systems with time-sync
- Start-Pause-Stop Data Recording
- Pre-trigger Data Recording in circular buffers
- Adaptable signal front-ends
- Read/write compatible with Linux Software-RAID
Scalability
MLE’s Fast FPGA RAID supports a wide range of NVMe SSDs and can be scaled from M.2 SSDs for small and light-weight embedded systems up to large 19” racks using high-performance U.2 or U.3 SSDs. Scalability also includes selecting from different SSD capacities and Drive-Writes-per-Day (DWPD) models. Here a table of possible recording times in minutes:
| Recording Speed (Gbps) | ||||||||
| Storage (TiB) | 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | |
| 5 | 7.2 | 4.8 | 3.6 | 2.9 | 2.4 | 2 | 1.8 | |
| 10 | 14.3 | 9.5 | 7.2 | 5.7 | 4.8 | 4.1 | 3.6 | |
| 15 | 21.5 | 14.3 | 10.7 | 8.6 | 7.2 | 6.1 | 5.4 | |
| 20 | 28.6 | 19.1 | 14.3 | 11.5 | 9.5 | 8.2 | 7.2 | |
| 25 | 35.8 | 23.9 | 17.9 | 14.3 | 11.9 | 10.2 | 8.9 | |
| 30 | 42.9 | 28.6 | 21.5 | 17.2 | 14.3 | 12.3 | 10.7 | |
| 35 | 50.1 | 33.4 | 25.1 | 20.0 | 16.7 | 14.3 | 12.5 | |
| 40 | 57.3 | 38.2 | 28.6 | 22.9 | 19.1 | 16.4 | 14.3 | |
| 45 | 64.4 | 42.9 | 32.2 | 25.8 | 21.5 | 18.4 | 16.1 | |
| 50 | 71.6 | 47.7 | 35.8 | 28.6 | 23.9 | 20.5 | 17.9 | |
| Recording Time in Minute(s) | ||||||||
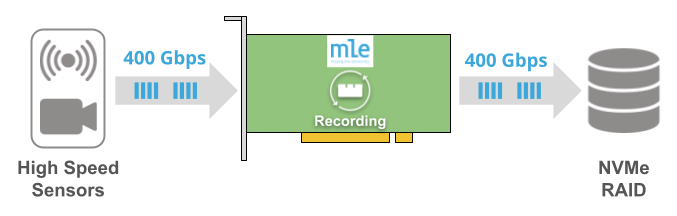
FFRAID High Speed Data Recording Use Cases
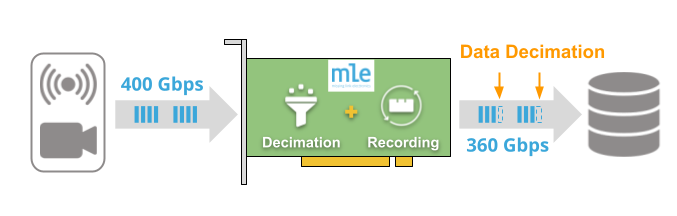
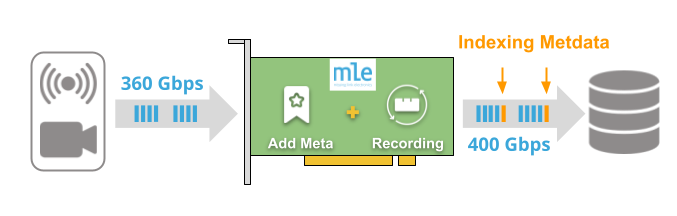
Besides record/replay of raw data we support data-in-motion pre- and post-processing that enables you to add your custom algorithms for indexing and metadata generation, on-the-fly data decimation, or running in “spy-mode” as a transparent data proxy.
- Ingress data from the high-speed sensors are transferred and recorded at-speed and as-is onto the Fast FPGA RAID.
Exemplary Evaluation Reference Design of Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID)
The implementation example of MLE 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID is built with AMD EPYC server-grade motherboard, NVMe RAID FPGA cards, and U.3 SSDs. This evaluation reference design is available now for testing with your front-end devices or SSDs.
Test with Your Front-End Device Now!
Test with Your SSDs Now!
100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID Turnkey System




InoNet Fast FPGA RAID System
- “Plug-and play” solution
- Support data recording at 100/200/400Gbps
- Support multiple SSD options
- Customizable I/O front-end
- QuickTray for SSD hotswap (optional)
- Multiple system options for lab, tabletop, datacenter, and automotive recording applications
Pricing
MLE’s license fee structure reflects the needs for best-in-class price/performance ratio for 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID:
| Product Name | Deliverables | Example Pricing |
|---|---|---|
Evaluation Reference Design (ERD) | Available upon request as FPGA design project, with optional customizations (different target device, different transceivers, etc) | Upon Request |
Turnkey System | Completely hardware-software integrated ready-to-use system, available sizes from medium-sized embedded PC to 19″ rack mount, lab-use or ruggedized. You can bring your own SSDs, or choose SSDs from our many options depending on the storage capacity required. | Starting at $14,800.- (depends on FPGA device, line rate, and SSDs) |
| Fast FPGA RAID Card | Fast FPGA RAID Card based on off-the-shelf 3rd party FPGA cards, including AMD Alveo U50 / U55C with Ultrascale+ and HBM, AMD Alveo V80 with Versal and HBM, and Intel/Altera Agilex 7 AGF014 with DDR4. | Starting at $8,000.- |
Documentation
- FPGA Based 400GBit/s Data Recorder – Insight into Different Pitfalls and Design Choices
- Linux ZynqMP PS-PCIe Root Port Driver (A software-only, non-accelerated alternative described by the Xilinx Wiki)
- Example designs on GitHub from Opsero (for PS-based NVMe supporting various FPGA and MPSoC evaluation boards)
Frequently Asked Questions
Does the "100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID)" data recorder, support file systems?
No, the MLE 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID data recorder is so-called Block Storage. So, no file systems are not supported. For each data transfer the user application logic selects a start and maximum end address, and then data is written to flash in a linear fashion. This achieves best performance and avoids write amplifications.
Does the "100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID)" data recorder support drive partitions?
Partitions are not explicitly supported. However, the user application logic can use the 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID data recorder to read the SSD’s partition table and then set up transfers with start and maximum end address to be aligned to partitions.
Does the "100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID)" data recorder support NVMe namespaces?
Only one single namespace is supported per SSD.
How many SSDs can be connected to the "100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID)" data recorder?
The standards for the 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID data recorder is 4/8/16 SSDs. The number of SSDs can be adjusted to your application within certain limits, for example: the accumulated sustained write speed should be faster then the incoming data stream, or to many SSDs can cause latency issues. However, we can customize the 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID data recorder for your application to support more complex PCIe topologies. Please ask us for more details.
How many NVMe IO Queues does the "100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID)" data recorder support and what is the depth of the NVMe IO Queue?
The 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID data recorder currently supports one single IO Queue per SSD. This IO Queue can have up to 128 entries, each with up to 128 KiB data. I.e. you can have up to 16 MiB of “data in flight” per SSD. If needed, we can change the depth and size of this IO Queue. However, given the needs of streaming applications increasing the number of IO Queues may not be advantageous.
Does the "100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID)" data recorder support PCIe Peer-to-Peer?
Yes, this is supported. Peer-to-Peer transfers can be very attractive as it frees up the host CPU. Team MLE can customize the 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID data recorder for your application to support many more complex PCIe topologies, including multiple direct-attached SSDs, multiple SSDs connected via a 3rd party PCIe switch chip, including PCIe Peer-to-Peer. Please ask us for more details.
What are the user interfaces of the "100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID)" data recorder?
The 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID data recorder can be configured via an AXI4-Lite register space which can also be handled by a provided Linux handler. This register space is also used to set up and control streaming transfers. The actual data exchange then is handled via an AXI4-Stream master and slave. Some GPIO style status signals for informational purposes, like LEDs, are provided as well. This is documented in our developers guide.
How many parallel streams can be processed?
Currently, the 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID) data recorder handles 16 independent data streams. To save resources, the number of streams can be reduced without loosing the overall performance by widening the data paths.
Does the "100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID)" data recorder support m.2 PCIe connectivity?
Yes. Because the 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID data recorder is agnostic to the formfactor of your SSD m.2, u.3/u.3, EDSFF and so on are supported, as long as your SSD “speaks the NVMe protocol” and not SATA nor SAS.
What are the best SSDs to use and from which vendor?
While, again, the 100/200/400G Fast FPGA RAID (FFRAID) data recorder is compatible to work with any NVMe SSD, there are a couple of other aspects to keep in mind when selecting an NVMe SSD: Noise, vibration, harshness, temperature throttling, local RAM buffers, SLC, MLC, TLC, QLC, 3D-XPoint, etc. To enable our customers to deliver dependable performance solutions, we have worked with a set of 3rd party SSD vendors and would be happy to give you technical guidance in your project. Please inquire.