Security & Trust
Security & Trust
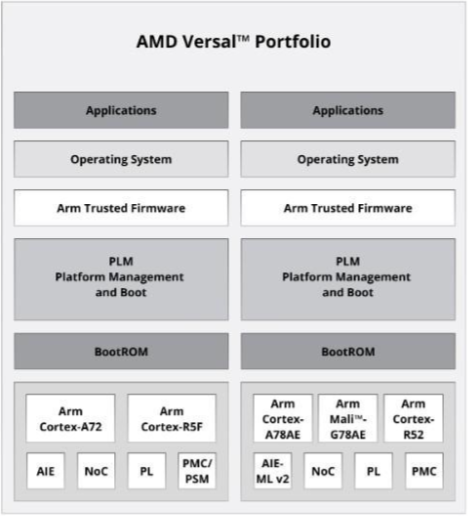
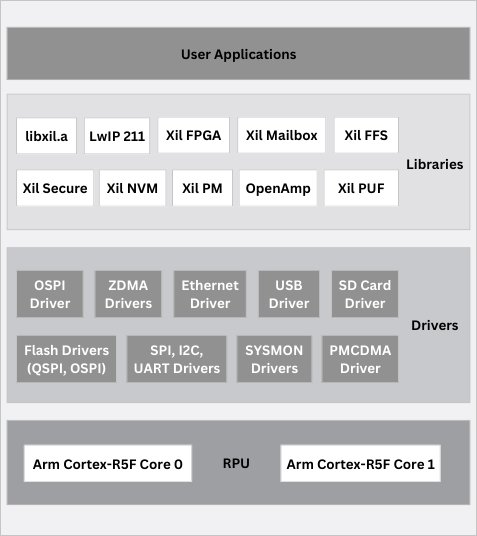
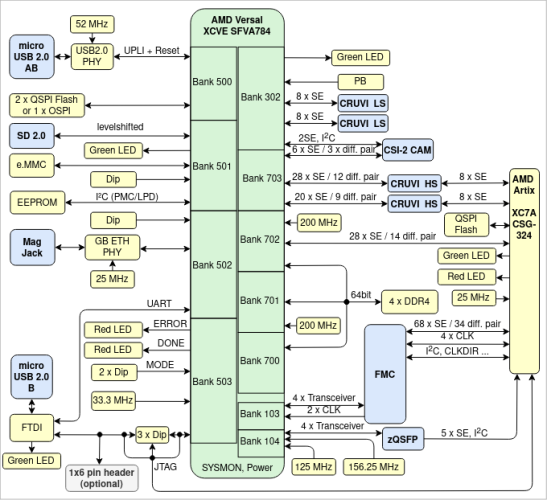
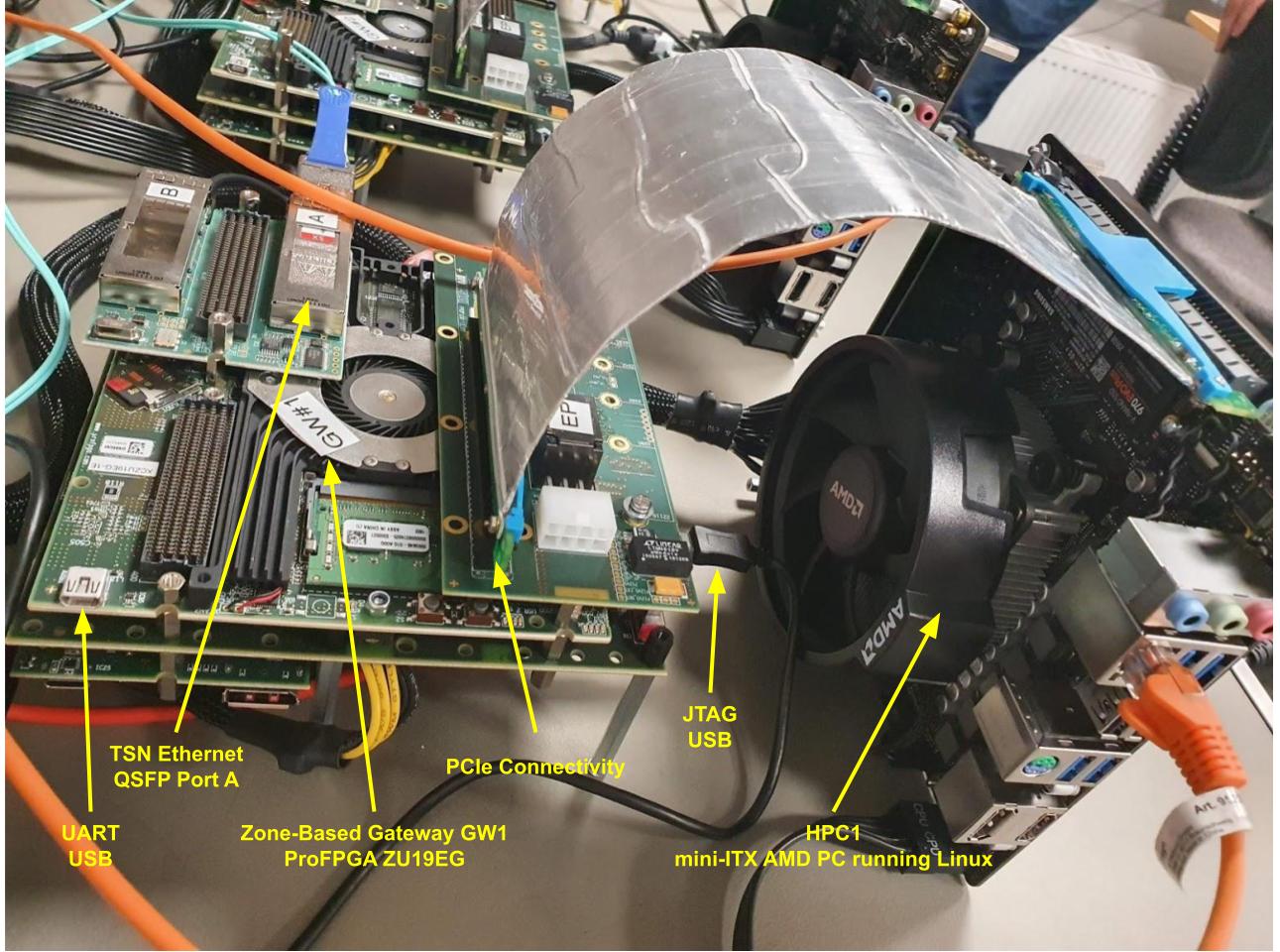
FPGA-Based Security Solutions
Since October 2024 the European Union has adopted the Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) which covers all products that are directly or indirectly connected to other devices or networks, including those requiring high-speed, low latency data transfer.
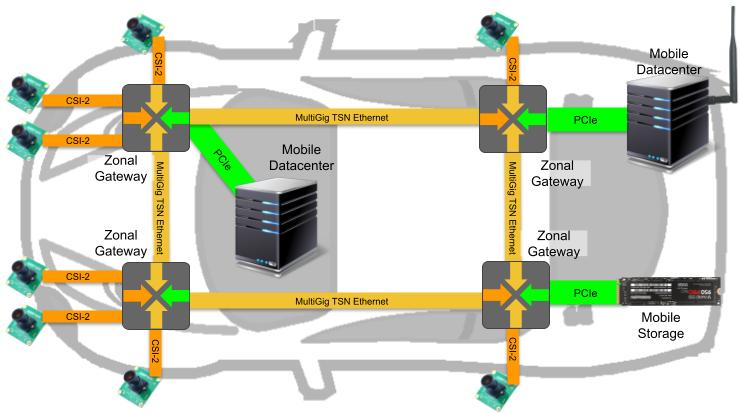
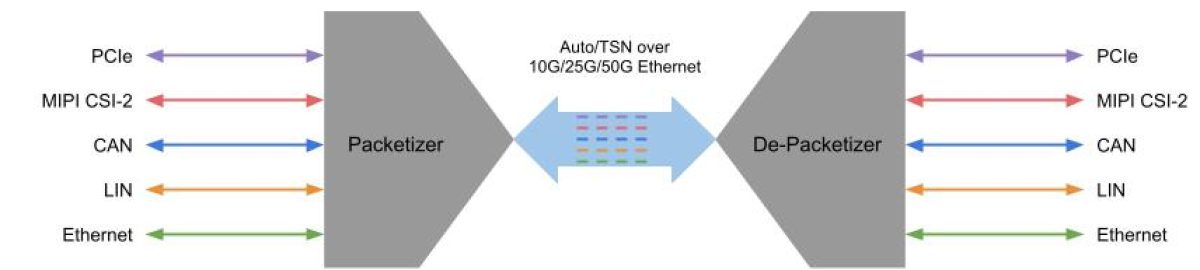
To help customers meet these new cybersecurity requirements, MLE provides a range of security solutions, including OP-TEE, Smart Data Diodes, Secure or Encrypted Networking, on top of network accelerators and NVMe accelerators for both modern and legacy FPGA systems.
OP-TEE
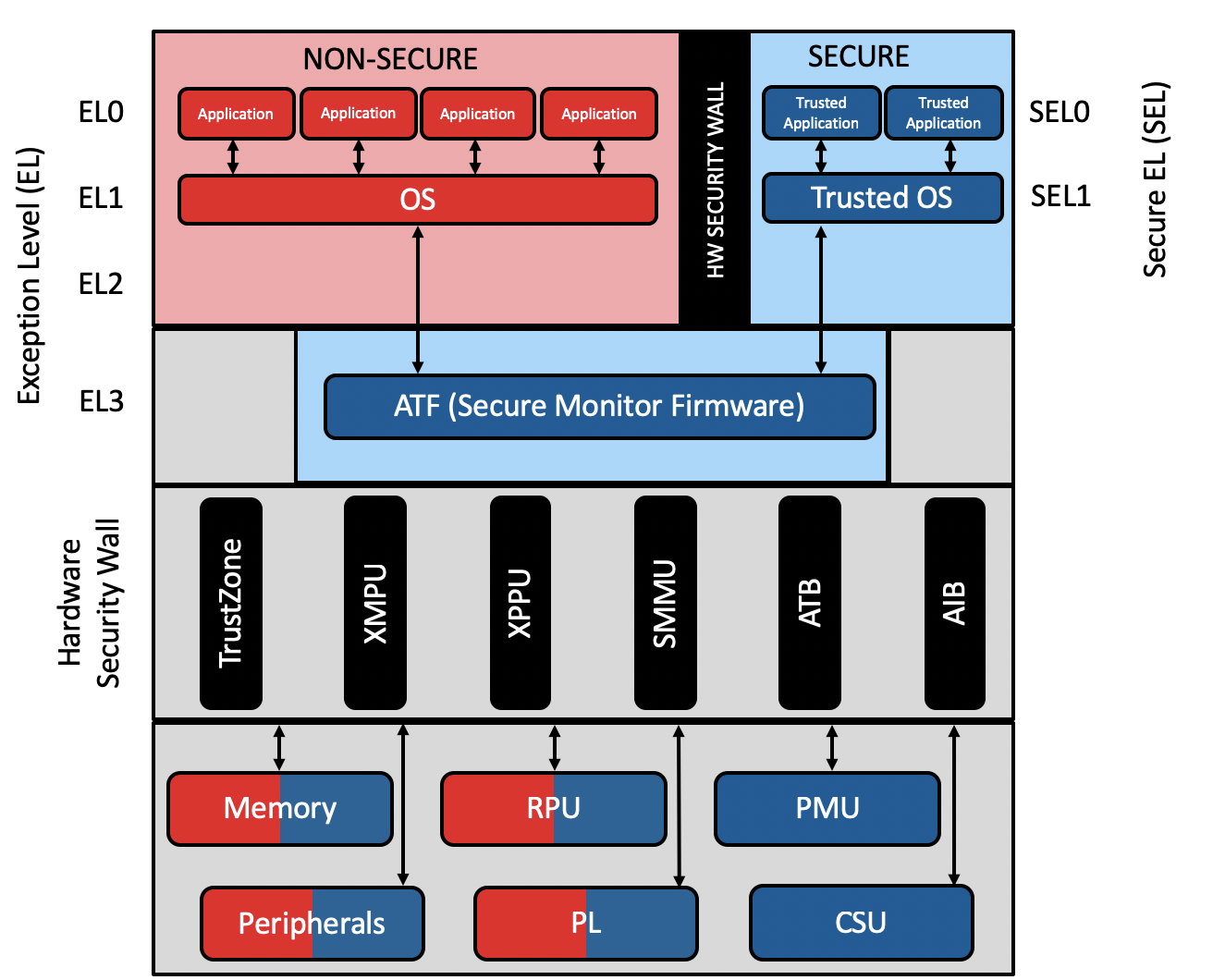
Open Portable Trusted Execution Environment
The Open Portable Trusted Execution Environment (OP-TEE) is an open-source, small, secure operating system which, after authentication and decryption, gets loaded in a secured area in the memory. MLE OP-TEE solutions for AMD/Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC / RFSoC and Versal include device-specific optimizations, customization and product life cycle support.
Smart Data Diodes
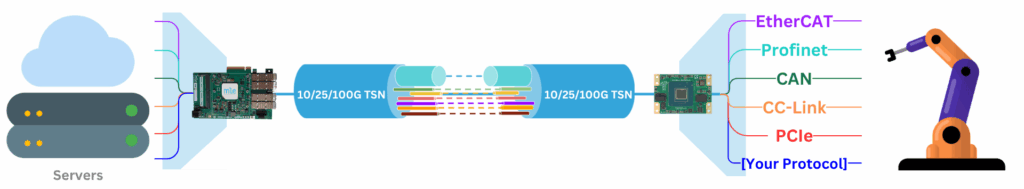
MLE combines Network Accelerators with Smart Data Diodes to enable secure, high-speed data transfer and video streaming between networks with different security classifications.
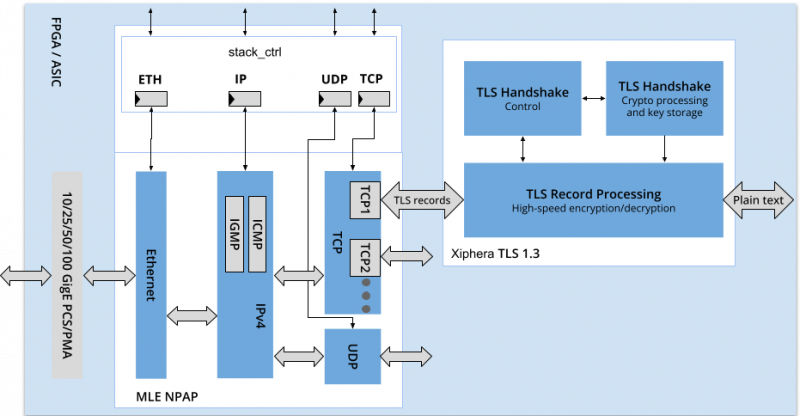
MLE partners with Xiphera, a leading provider of cryptographic IP solutions, to deliver multi-level security capabilities built on top of MLE’s network accelerators, enabling secure, reliable, and high-speed data transfer across industrial, data center, aerospace, defense, transportation, telecommunications, and financial applications.
Upgrade Legacy Systems

MLE has started to work with FPGA vendors on system upgrades and “bump-on-the-wire” solutions to bring security to upgrade existing legacy systems with better security.